Vascular Ring Program Overview
Vascular ring is a congenital aortic arch anomaly where the aorta and surrounding blood vessels develop abnormally, forming a ring-like structure that encircles the trachea and esophagus. A vascular ring can lead to breathing and swallowing difficulties as well as heart problems.
Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego specializes in the treatment of vascular rings, offering various surgical and non-surgical options under the leadership of Matthew Brigger, MD, chief of the Division of Otolaryngology, and John Nigro, MD, chief of the Division of Cardiac Surgery and Director of the Heart Institute.
At Rady Children’s, our specialists are here to help identify and treat vascular rings—whether it’s a complete vascular ring or an incomplete one. By understanding your child’s unique vascular structure, we can address any heart problems or related heart defects early and work together toward the best outcome.
Pediatric Aerodigestive Vascular Ring Program at Rady Children’s Hospital

Sage received world-class care from our Otolaryngology team at Rady Children’s Hospital. Read the Story.
Rady Children’s Hospital provides a comprehensive, tailored approach for each patient through our Aerodigestive Vascular Ring Program. A multidisciplinary team of experts from Otolaryngology (ENT), pulmonary, gastroenterology, cardiology, speech-language pathology, occupational therapy, and nutrition will assess your child. The team of medical professionals conducts a detailed history and examination, utilizes advanced imaging and diagnostic tests, and develops an individualized treatment plan.
Additional tests may include a Triple endoscopy, CT imaging, Pulmonary Function Testing, and swallow studies. After our thorough assessment, a 3D model is created of your child’s vascular ring. Depending on the severity of your child’s symptoms, we may discuss your child’s case at our monthly conference, which includes specialists from the Aerodigestive team, Cardiovascular Surgery, Radiology, and a 3D printing scientist. This comprehensive team approach allows us to provide the best individualized care possible. We continue to manage your child’s care long after any surgery is performed and work with you to create long-standing success.
This detailed evaluation helps identify specific vascular anomalies, such as aortic arch anomalies or pulmonary artery slings, which may be contributing to your child’s condition. If your child requires vascular ring repair, our team carefully considers factors like a left aortic arch, left subclavian artery, or right subclavian artery to plan the most effective approach. By addressing congenital heart disease and other related conditions, our specialists provide expert care, including heart surgery if necessary, to ensure the best outcomes for your child.
What Is a Vascular Ring?
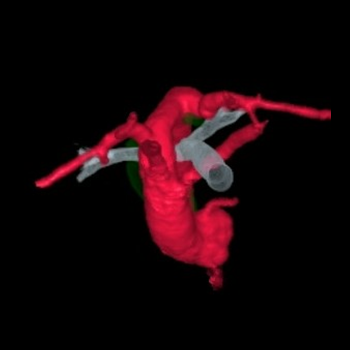
A vascular ring occurs when the aorta and its branching blood vessels are improperly formed, causing compression of the trachea and esophagus. Vascular rings occur in approximately 1 in 2,500 births, with a higher prevalence in boys. They are usually isolated, but can also happen with other congenital heart defects. Some patients may have associated genetic conditions, the most common of which is 22q11 deletion syndrome (also known as DiGeorge syndrome).
There are two common types of vascular rings:
- Double aortic arch: Two separate aortic arches (right and left) wrap around each side of the trachea and esophagus.
- Right aortic arch with aberrant left subclavian artery: The aortic arch is on the right side of the chest, but the left subclavian artery arises behind it and is connected by a left-sided ligament, potentially compressing the trachea and esophagus.
Symptoms & Diagnosis
A child may or may not have symptoms depending on how tight the vascular ring is around the trachea and esophagus. Some children and adults may have no symptoms at all. Others may have symptoms due to airway or esophageal compression.
Some common symptoms include:
- Noisy breathing (stridor)
- Difficulty breathing
- Frequent respiratory infections with prolonged recovery
- Chronic cough
- Difficulty swallowing foods
- Poor feeding and/or frequent vomiting
Vascular rings can be diagnosed based on symptoms or findings on a chest X-ray or echocardiogram. If a vascular ring is suspected in utero, you may meet with our Fetal Cardiology team to discuss possible impacts on pregnancy and delivery. Your provider may also recommend a CT scan or MRI of the chest and/or heart to examine the abnormal blood vessels, as well as the airway and esophagus.
Treatment and Management
At Rady Children’s Hospital, we believe that not all vascular rings need surgical repair, especially if a child is asymptomatic. However, for children experiencing symptoms, the primary treatment is surgery. Surgery is typically successful, and most children recover fully. The goal is to remove the abnormal ring of blood vessels that is compressing the trachea and esophagus.
If surgery is recommended, the cardiovascular surgeon will decide the best approach after reviewing all imaging. Approaches may include:
- A thoracotomy (accessing the chest wall from the side between the ribs)
- A sternotomy (dividing the breastbone to access the chest cavity)
Techniques to resect the vascular ring can include takedown of the vessels or ligaments, re-implanting an abnormal subclavian artery, or re-positioning the aorta.
After your child’s surgery, our health care professionals continue to manage your child’s care through our outpatient clinic to ensure improvements in breathing and feeding for optimal success.
Steps for Vascular Ring Treatment and Management
- Evaluation and Diagnosis: Detailed assessments, including imaging (CT, MRI, or endoscopy), confirm the vascular anomaly. This helps identify any tracheoesophageal compression or additional heart defects.
- Treatment Planning: If symptoms are present, surgery is recommended. The cardiovascular surgeon reviews diagnostics to determine the best surgical approach.
- Surgical Approach: The surgeon may choose:
- Thoracotomy: Accessing the chest through the side (between the ribs).
- Sternotomy: Dividing the breastbone to access the chest cavity.
- Surgical Repair: Resecting or removing the vessels or ligaments causing compression, re-implanting abnormal subclavian arteries if needed, and re-positioning the aorta.
- Post-Surgical Care: Ongoing monitoring and follow-up in our outpatient clinic to ensure improvements in breathing, feeding, and overall health.
Meet Our Team
Matthew Brigger, MD, Division Chief of Otolaryngology

Dr. Brigger is chief of the Division of Otolaryngology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego and a professor of surgery at UC San Diego School of Medicine. His clinical interests focus on diseases of the upper aerodigestive tract, with a particular emphasis on surgical management of breathing and swallowing disorders in children.
He is a pioneer of the Pediatric Aerodigestive Vascular Ring Program at Rady Children’s Hospital, with the goal of providing comprehensive and accessible care to children with this ailment.
Request an Appointment for Diagnosing Vascular Rings
Access our referral forms below to request an appointment at Rady Children’s Hospital. If you have any questions, please contact our Center for Pediatric Aerodigestive Disorders and Airway Surgery Nurse Coordinator at 858-966-8336 ext. 223403.
Contact Us
Pediatric Aerodigestive Vascular Ring Program
Rady Children’s Hospital
Otolaryngology Clinic
Medical Office Building 1st Floor
3030 Children’s Way
San Diego, CA 92123
Tel: (858) 966-1700 ext 223403
Fax: (858) 966-4062
Email: RadyAerodigestive@rchsd.org